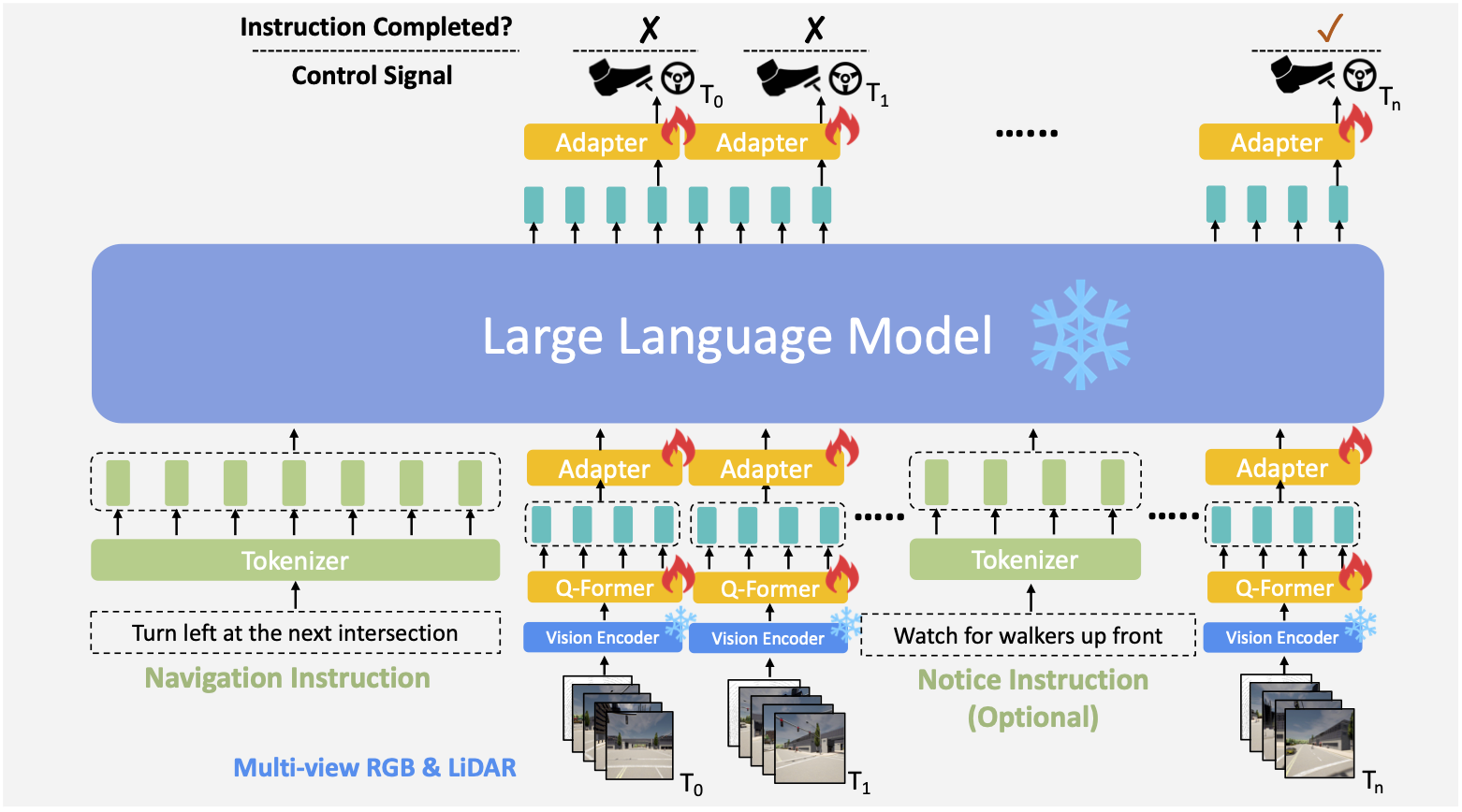
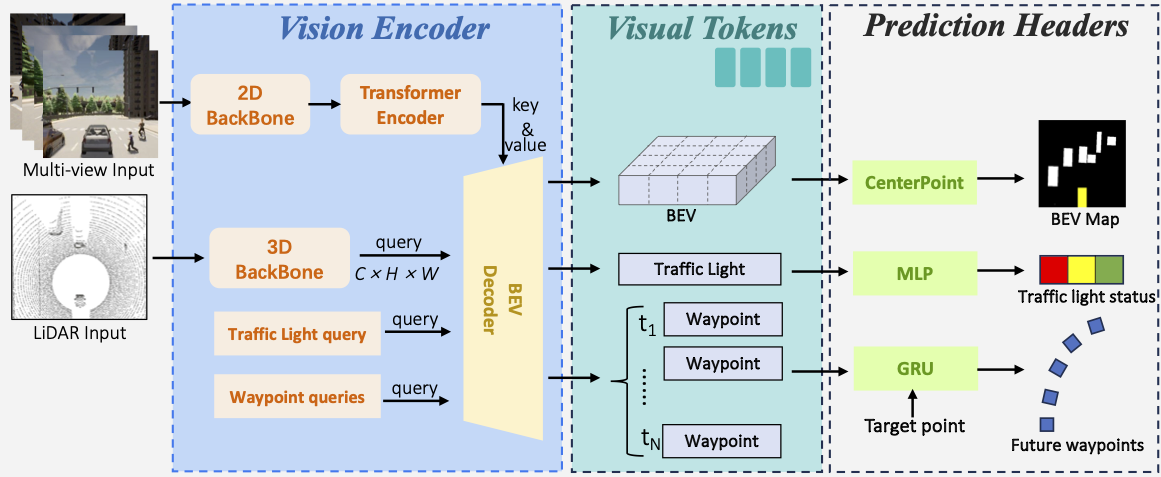
 LMDrive Dataset
LMDrive Dataset
We provide a dataset with about 64K data clips, where each clip includes one navigation instruction, several notice instructions, a sequence of multi-modal multi-view sensor data, and control signals. The duration of the clip spans from 2 to 20 seconds.
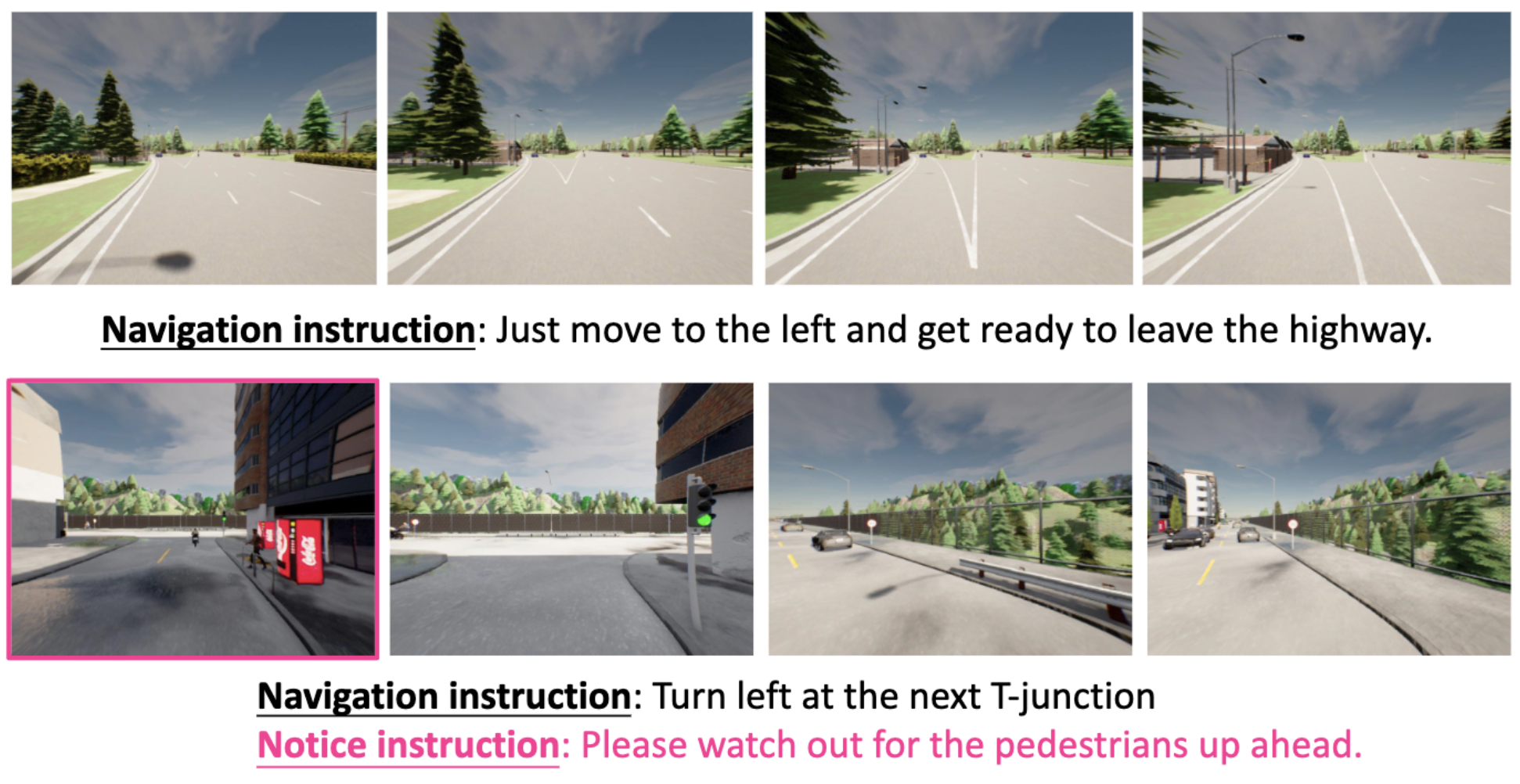
Two examples of the collected data with corresponding labeled navigation instructions and optional notice instructions.
| Type | Three randomly chosen instructions of each instruction type |
|---|---|
| Follow | Maintain your current course until the upcoming intersection. In [x] meters, switch to left lane. Ease on to the left and get set to join the highway. |
| Turn | After [x] meters, take a left. At the next intersection, just keep heading straight, no turn. You’ll be turning left at the next T-junction, alright? |
| Others | Feel free to start driving. Slow down now. Head to the point, next one’s [x] meters ahead, [y] meters left/right. |
| Notice | Watch for walkers up front. Just a heads up, there’s a bike ahead. Please be aware of the red traffic signal directly in front of you. |
Examples of considered navigation instructions (follow, turn, others) and notice instructions. [x] and [y] represent the float number for a specific distance.